Log & Common Errors
This page gives you guidance on how to interpret one of the below error messages.
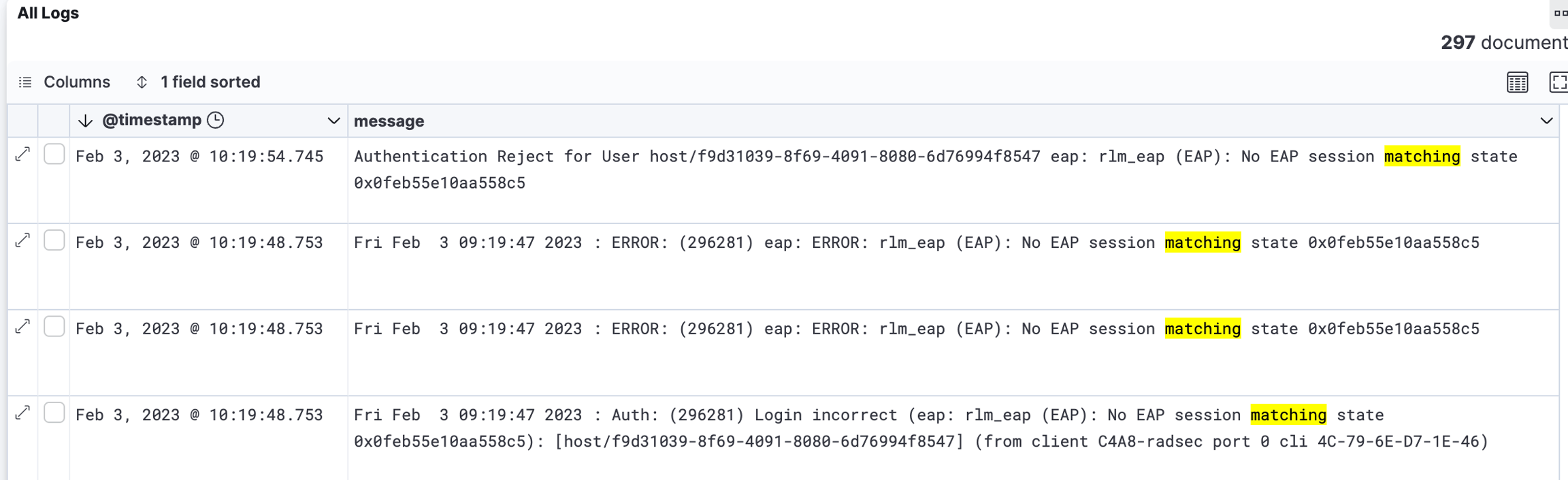
No EAP session matching state
Severity: Low / No Impact
Corresponding error messages:
"No EAP session matching state"
"Unable to set parent list"
The RADIUS protocol is stateless and since it is normally transmitted over UDP, it has to validate if all packages have arrived, if their integrity persists, if they can be correctly assembled in the correct order, etc., essentially mitigating the flaws of the UDP protocol.
Each authentication request goes through a process of steps that must be performed (e.g. association, request, challenge, challenge-response). For these steps, both sides (client and server) have a state that is included in the packet sent and a state that is stored locally. These states must match the step that client and server are currently in, respectively.
The error message indicates that one of the actors (client, server) has sent or received a packet that does not match the expected state. These errors happen from time to time as UDP cannot guarantee that packets are always delivered (correctly or at all). In most cases this is not a problem because the RADIUS protocol handles these errors and re-initiates the connection without the computer that is trying to log in noticing.
If the devices are able to connect eventually without noticeable delays, such errors can be ignored. If this is not the case, try increasing your EAP timeouts.
Proxy Session Resumption
Severity: Low / No Impact
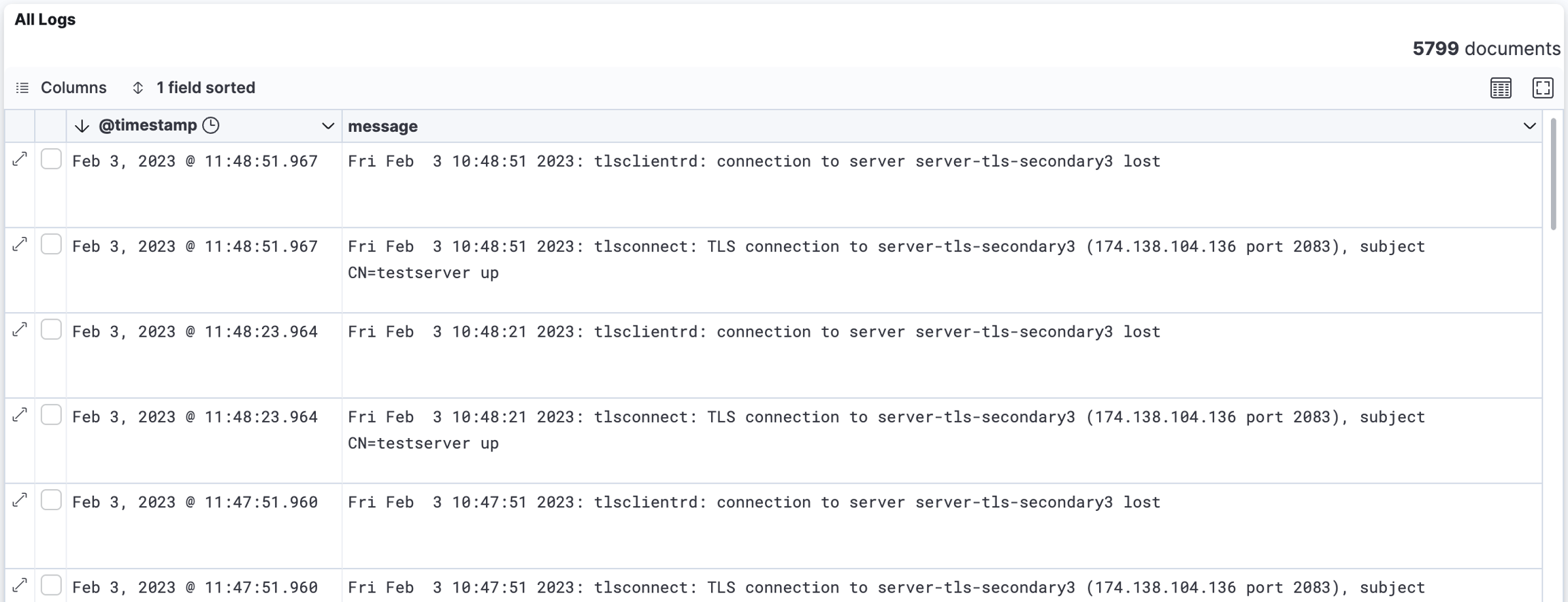
Your proxies will create a TCP session with your RadSec server(s). These sessions have to be reinitiated every 30 seconds. As long as there is no error within those messages, these log entries are expected.
Error in error
Severity: Low / No Impact

Since your RadSec server(s) are globally available, anyone on the Internet can try to connect to them, e.g. using a TCP handshake. If no valid (mututal) TLS connection can be established (which only works if the connecting entity presents a trusted RadSec client certificate), this error message is generated and expcted.
Since RADIUSaaS cannot distinguish between someone crawling/port-scanning servers on the internet and a legit authenticator that is simply misconfigured, RADIUSaaS does not suppress these log entries. This means, if your infrastructure is working fine, you may ignore these log entries.
Certificate status was revoked previously
Severity: Low / No Impact

If a certificate is found to be revoked, this status will be cached for 2 minutes. Additional attempts to authenticate this certificate will directly be rejected without performing another OCSP request. This is done to reduce the load on the OCSP responder.
The Verify-Description field will contain the correlation ID of the initial rejected request.

Last updated
Was this helpful?