FortiNet
To use the RadSec feature on your FortiGate for WiFi (with FortiAPs), firmware FortiOS 7.6.0 or later is required on the FortiGate.
Prepare certificates
To establish a valid RadSec connection, your Access Points must trust the RADIUS Server Certificate and your RADIUS server must trust your RadSec Client Certificate. To achieve this,
Download the root certificate of the CA that has issued your active RADIUS Server Certificate as described here.
Create a RadSec Client Certificate for your WAPs (centrally managed via FortiGate). If you are using SCEPman Certificate Master, the process is described here. FortiGate accepts the PKCS#12 format for RadSec client certificates.
Ensure to monitor the expiry of your RadSec Client Certificate and renew it in due time to prevent service interruptions.
Add the root certificate of the CA that has issued the RadSec Client Certificate to your RADIUS instance as described here and select RadSec under Use for. In case the RadSec Client Certificate has been issued by SCEPman and you already trust the SCEPman Root CA for client authentication, simply edit the trusted SCEPman Root CA certificate and select Both under Use for.
FortiGate configuration
Below settings are the necessary settings to establish a functional RadSec connection with our service. Configure any other settings at your discretion.
Via UI
To configure RadSec on your FortiGate UI please follow the steps:
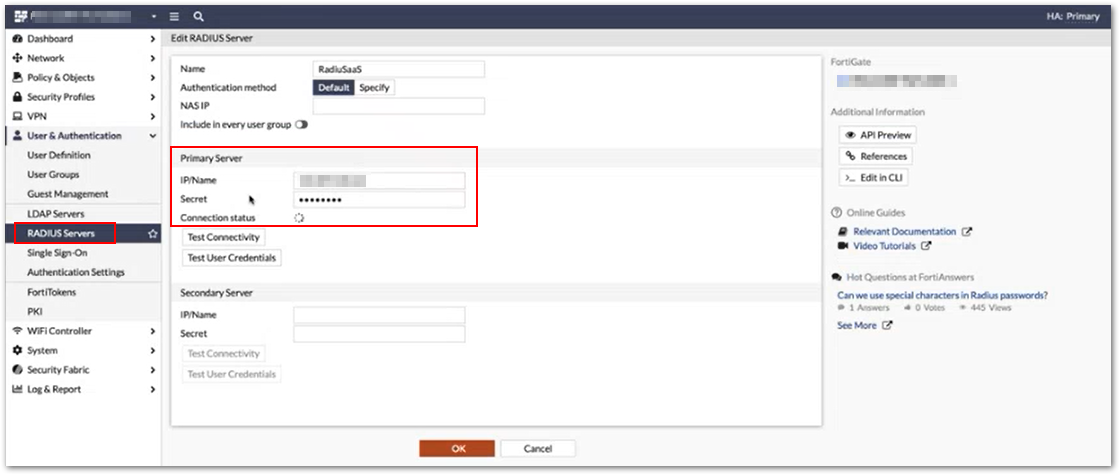
Create a new RADIUS Server and add your RadSec server IP address under IP/Name. For the Secret, use "radsec".
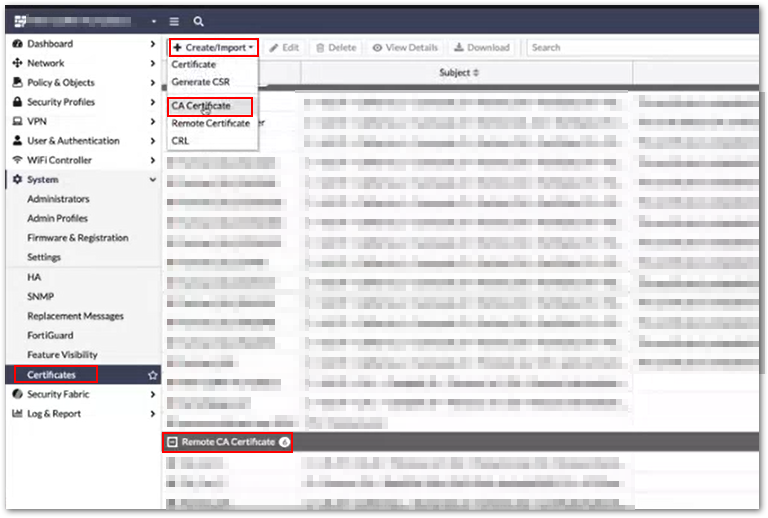
Import the root CA of your RADIUS Server Certificate to the FortiGate Certificates under System > Certificates > Import > CA Certificate. The imported root CA will be listed under Remote CA Certificate.
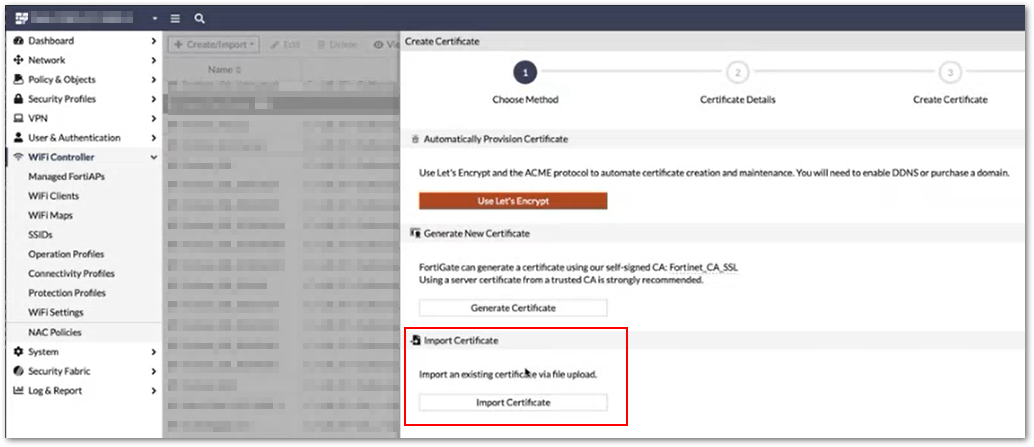
Import the RadSec Client Certificate to your FortiGate under System > Certificates > Import > Certificate.
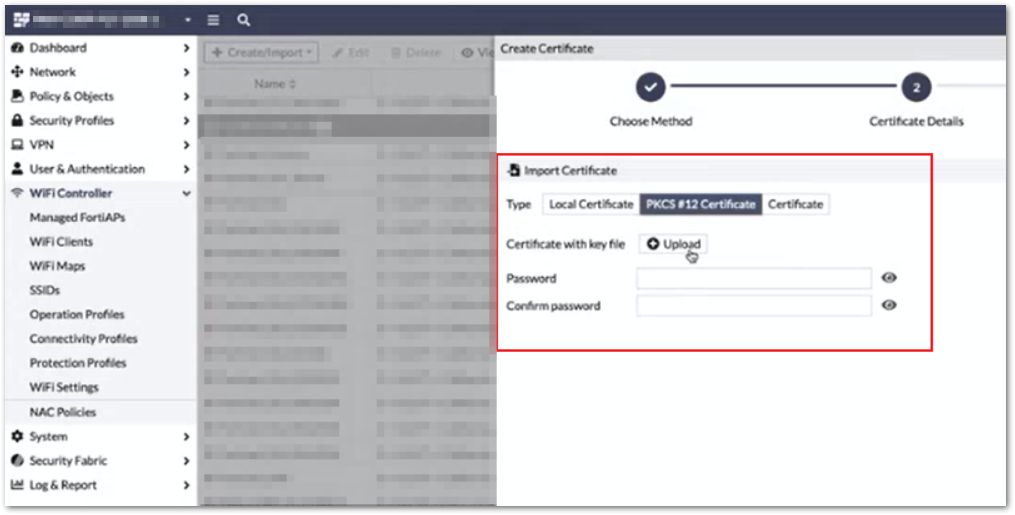
Modify the RADIUS server configuration in your FortiGate to use it as RadSec client certificate.
If enabled, please disable the server-identity-check in your FortiGate RADIUS server configuration.
Via command line
To configure RadSec on your FortiGate using the command line, please use these below sets of instructions:
RADIUS server configuration
WiFi SSID configuration
References
Link to FortiGate's documentation for the RadSec configuration: https://docs.fortinet.com/document/fortigate/7.6.0/administration-guide/729374/configuring-a-radsec-client
Last updated
Was this helpful?